Understanding Computer Fundamentals And Office Automation Software
COURTESY :- vrindawan.in
Wikipedia
A computer is a digital electronic machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a “complete” computer that includes the hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for “full” operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster.

A broad range of industrial and consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devices like personal computers and mobile devices like smartphones. Computers power the Internet, which links billions of other computers and users.
Early computers were meant to be used only for calculations. Simple manual instruments like the abacus have aided people in doing calculations since ancient times. Early in the Industrial Revolution, some mechanical devices were built to automate long tedious tasks, such as guiding patterns for looms. More sophisticated electrical machines did specialized analog calculations in the early 20th century. The first digital electronic calculating machines were developed during World War II. The first semiconductor transistors in the late 1940s were followed by the silicon-based MOSFET (MOS transistor) and monolithic integrated circuit (IC) chip technologies in the late 1950s, leading to the microprocessor and the microcomputer revolution in the 1970s. The speed, power and versatility of computers have been increasing dramatically ever since then, with transistor counts increasing at a rapid pace (as predicted by Moore’s law), leading to the Digital Revolution during the late 20th to early 21st centuries.
Conventionally, a modern computer consists of at least one processing element, typically a central processing unit (CPU) in the form of a microprocessor, along with some type of computer memory, typically semiconductor memory chips. The processing element carries out arithmetic and logical operations, and a sequencing and control unit can change the order of operations in response to stored information. Peripheral devices include input devices (keyboards, mice, joystick, etc.), output devices (monitor screens, printers, etc.), and input/output devices that perform both functions (e.g., the 2000s-era touchscreen). Peripheral devices allow information to be retrieved from an external source and they enable the result of operations to be saved and retrieved.
According to the Oxford English Dictionary, the first known use of computer was in a 1613 book called The Yong Mans Gleanings by the English writer Richard Brathwait: “I haue [sic] read the truest computer of Times, and the best Arithmetician that euer [sic] breathed, and he reduceth thy dayes into a short number.” This usage of the term referred to a human computer, a person who carried out calculations or computations. The word continued with the same meaning until the middle of the 20th century. During the latter part of this period women were often hired as computers because they could be paid less than their male counterparts. By 1943, most human computers were women.
The Online Etymology Dictionary gives the first attested use of computer in the 1640s, meaning ‘one who calculates’; this is an “agent noun from compute (v.)”. The Online Etymology Dictionary states that the use of the term to mean “‘calculating machine’ (of any type) is from 1897.” The Online Etymology Dictionary indicates that the “modern use” of the term, to mean ‘programmable digital electronic computer’ dates from “1945 under this name; [in a] theoretical [sense] from 1937, as Turing machine“.
Devices have been used to aid computation for thousands of years, mostly using one-to-one correspondence with fingers. The earliest counting device was probably a form of tally stick. Later record keeping aids throughout the Fertile Crescent included calculi (clay spheres, cones, etc.) which represented counts of items, probably livestock or grains, sealed in hollow unbaked clay containers. The use of counting rods is one example.
The abacus was initially used for arithmetic tasks. The Roman abacus was developed from devices used in Babylonia as early as 2400 BC. Since then, many other forms of reckoning boards or tables have been invented. In a medieval European counting house, a checkered cloth would be placed on a table, and markers moved around on it according to certain rules, as an aid to calculating sums of money.
The Antikythera mechanism is believed to be the earliest known mechanical analog computer, according to Derek J. de Solla Price. It was designed to calculate astronomical positions. It was discovered in 1901 in the Antikythera wreck off the Greek island of Antikythera, between Kythera and Crete, and has been dated to approximately c. 100 BC. Devices of comparable complexity to the Antikythera mechanism would not reappear until the fourteenth century.
Many mechanical aids to calculation and measurement were constructed for astronomical and navigation use. The planisphere was a star chart invented by Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī in the early 11th century. The astrolabe was invented in the Hellenistic world in either the 1st or 2nd centuries BC and is often attributed to Hipparchus. A combination of the planisphere and dioptra, the astrolabe was effectively an analog computer capable of working out several different kinds of problems in spherical astronomy. An astrolabe incorporating a mechanical calendar computer and gear-wheels was invented by Abi Bakr of Isfahan, Persia in 1235. Abū Rayhān al-Bīrūnī invented the first mechanical geared lunisolar calendar astrolabe, an early fixed-wired knowledge processing machine with a gear train and gear-wheels, c. 1000 AD.
The sector, a calculating instrument used for solving problems in proportion, trigonometry, multiplication and division, and for various functions, such as squares and cube roots, was developed in the late 16th century and found application in gunnery, surveying and navigation.
The planimeter was a manual instrument to calculate the area of a closed figure by tracing over it with a mechanical linkage.
Office automation refers to the varied computer machinery and software used to digitally create, collect, store, manipulate, and relay office information needed for accomplishing basic tasks. Raw data storage, electronic transfer, and the management of electronic business information comprise the basic activities of an office automation system. Office automation helps in optimizing or automating existing office procedures.
The backbone of office automation is a local area network, which allows users to transfer data, mail and voice across the network. All office functions, including dictation, typing, filing, copying, fax, telex, microfilm and records management, telephone and telephone switchboard operations, fall into this category. Office automation was a popular term in the 1970s and 1980s as the desktop computer exploded onto the scene. Advantages of office automation include that it can get many tasks accomplished faster, it eliminates the need for a large staff, less storage is required to store data, and multiple people can update data simultaneously in the event of changes in schedule.
Businesses can easily purchase and stock their wares with the aid of technology. Many of the manual tasks that used to be done by hand can now be done through hand held devices and UPC and SKU coding. In the retail setting, automation also increases choice. Customers can easily process their payments through automated credit card machines and no longer have to wait in line for an employee to process and manually type in the credit card numbers.
Office payrolls have been automated, which means no one has to manually cut checks, and those checks that are cut can be printed through computer programs. Direct deposit can be automatically set up and this further reduces the manual process, and most employees who participate in direct deposit often find their paychecks come earlier than if they’d have to wait for their checks to be written and then cleared by the bank.
Other ways automation has reduced employee manpower on tasks is automated voice direction. Through the use of prompts, automated phone menus and directed calls, the need for employees to be dedicated to answer the phones has been reduced, and in some cases, eliminated.
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
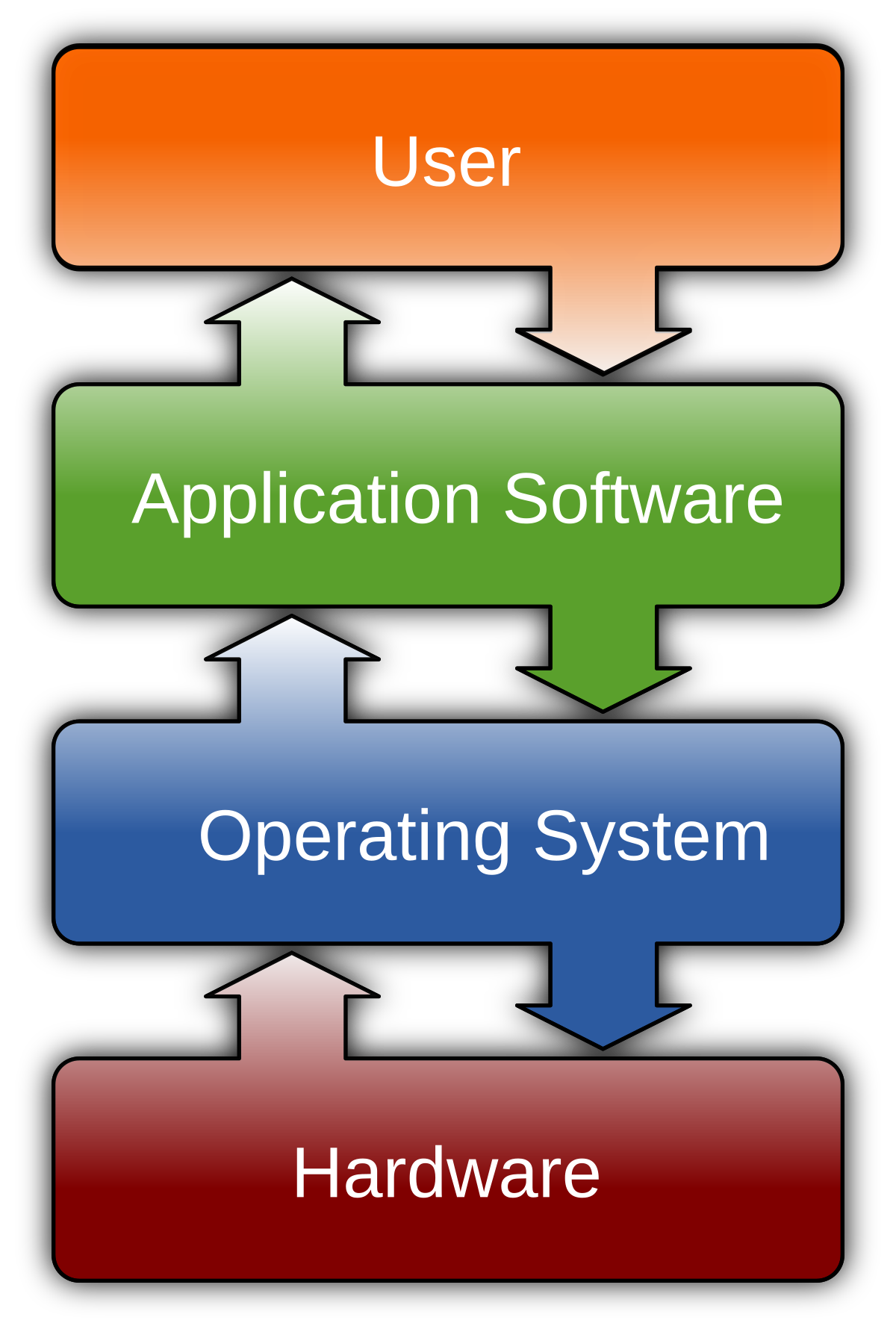
At the lowest programming level, executable code consists of machine language instructions supported by an individual processor—typically a central processing unit (CPU) or a graphics processing unit (GPU). Machine language consists of groups of binary values signifying processor instructions that change the state of the computer from its preceding state. For example, an instruction may change the value stored in a particular storage location in the computer—an effect that is not directly observable to the user. An instruction may also invoke one of many input or output operations, for example displaying some text on a computer screen; causing state changes which should be visible to the user. The processor executes the instructions in the order they are provided, unless it is instructed to “jump” to a different instruction, or is interrupted by the operating system. As of 2015, most personal computers, smartphone devices and servers have processors with multiple execution units or multiple processors performing computation together, and computing has become a much more concurrent activity than in the past.
The majority of software is written in high-level programming languages. They are easier and more efficient for programmers because they are closer to natural languages than machine languages. High-level languages are translated into machine language using a compiler or an interpreter or a combination of the two. Software may also be written in a low-level assembly language, which has a strong correspondence to the computer’s machine language instructions and is translated into machine language using an assembler.
An algorithm for what would have been the first piece of software was written by Ada Lovelace in the 19th century, for the planned Analytical Engine. She created proofs to show how the engine would calculate Bernoulli numbers. Because of the proofs and the algorithm, she is considered the first computer programmer.
The first theory about software, prior to the creation of computers as we know them today, was proposed by Alan Turing in his 1936 essay, On Computable Numbers, with an Application to the Entscheidungsproblem (decision problem). This eventually led to the creation of the academic fields of computer science and software engineering; both fields study software and its creation. Computer science is the theoretical study of computer and software (Turing’s essay is an example of computer science), whereas software engineering is the application of engineering principles to development of software.
In 2000, Fred Shapiro, a librarian at the Yale Law School, published a letter revealing that John Wilder Tukey’s 1958 paper “The Teaching of Concrete Mathematics” contained the earliest known usage of the term “software” found in a search of JSTOR’s electronic archives, predating the OED’s citation by two years. This led many to credit Tukey with coining the term, particularly in obituaries published that same year, although Tukey never claimed credit for any such coinage. In 1995, Paul Niquette claimed he had originally coined the term in October 1953, although he could not find any documents supporting his claim. The earliest known publication of the term “software” in an engineering context was in August 1953 by Richard R. Carhart, in a Rand Corporation Research Memorandum.
